The Human body is a work of art. Our immune system is a powerful, beautiful, and resilient machine that silently protects us every day.
What is an immune system?
Immune system is the body’s natural defense mechanism which is made up of special organs, cells & chemicals that fight infection (microbes). Together, they act as a personal shield to protect our health.
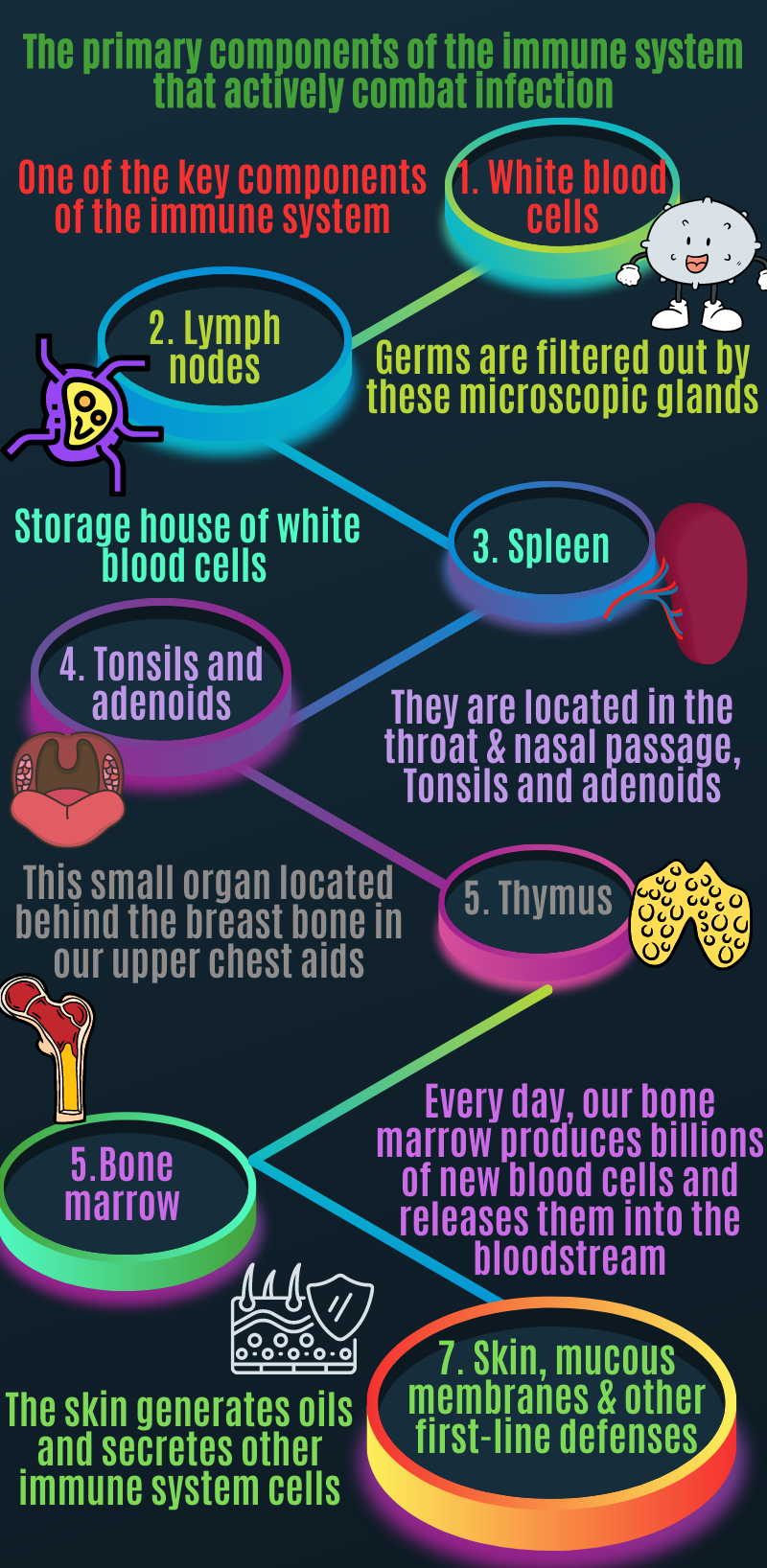
The primary components of the immune system that actively combat infection
- White blood cells: One of the key components of the immune system. White blood cells serve as an army to fight against harmful bacteria and viruses. The immune system contains various types of white blood cells that circulate in the blood and throughout our body or reside in specific tissues, waiting to be called into action.
- Lymph nodes: Germs are filtered out by these microscopic glands, which prevent them from spreading to other parts of the body. Immune cells in lymph nodes examine foreign pathogens that enter our bodies. They then activate, proliferate, and send the appropriate lymphocytes (white blood cells) to combat the invader.
- Spleen: Storage house of white blood cells that protect your body from foreign invaders are stored in it. Spleen also filters blood, eliminating any old or damaged red blood cells.
- Tonsils and adenoids: Since they are located in the throat & nasal passage, Tonsils and adenoids, can catch foreign invaders (such as bacteria or viruses) as soon as they enter our body. They have immune cells that make antibodies to protect you from foreign invaders that can cause throat and lungs infection.
- Thymus: This small organ located behind the breast bone in our upper chest aids in the maturation of a certain type of white blood cell.
- Bone marrow: Red blood cells, plasma cells, a variety of white blood cells, and other types of immune cells develop from stem cells in the spongy interior of bones. Every day, our bone marrow produces billions of new blood cells and releases them into the bloodstream.
- Skin, mucous membranes & other first-line defenses: Skin serves as the first line of defense in preventing & eradicating the germs before they enter our body. The skin generates oils and secretes other immune system cells. The respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive pathways are all lined with mucous membranes.
These all mucous membranes secrete mucus, which lubricates and moistens surfaces. Germs cling to mucus in the respiratory system and are then pushed out of the airways by cilia, which are hair-like structures
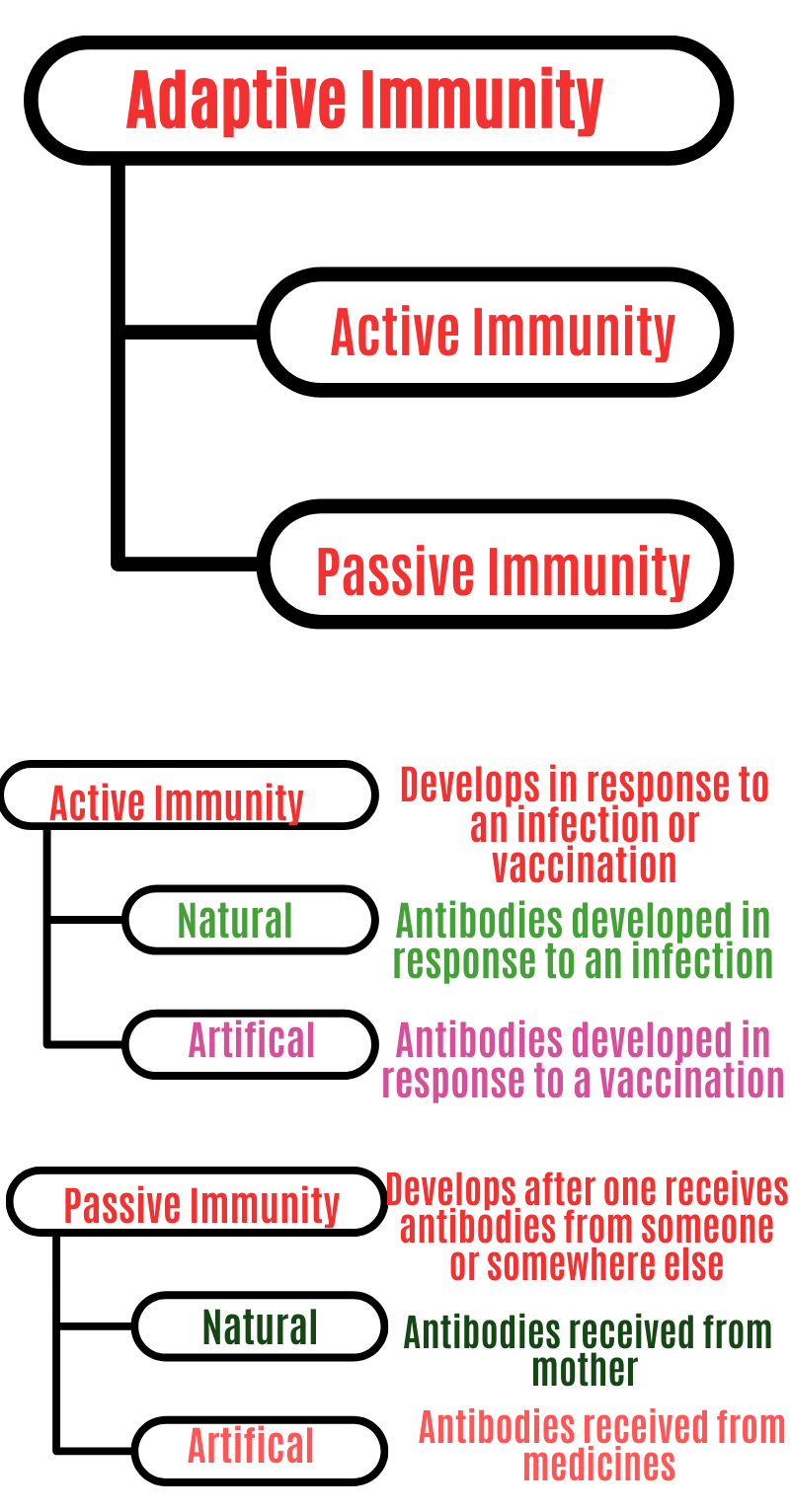
Types of Immunity
Major disorders of the immune system are
Immune system disorders occur when the immune system is not functioning properly.
Primary immune deficiency: Have a weakened immune system since birth
Acquired immune deficiency: Become ill with a disease that compromises your immune system.
Allergic reaction: Having an overactive immune system
Autoimmune disease: cause the body to attack and harm its tissues
Example of Primary immune deficiency
Severe combination immunodeficiency (SCID): is a kind of immunodeficiency that is present since birth. Infections caused by bacteria, viruses and fungi pose a persistent threat to children. This condition is also known as “bubble boy illness.”
Example of Acquired immune deficiency
AIDS or HIV: is an acquired viral infection that destroys the white blood cells and impairs the immune system, resulting in AIDS. The infections that most people can fight off can make people living with HIV / AIDS seriously ill. These types of infections are referred to as “opportunistic infections.”
Some examples of overactive immune systems are
- Asthma: Coughing, wheezing, and difficulty in breathing are all symptoms of Asthma. Common allergens like dust or pollen, as well as irritants like cigarette smoke, can trigger asthma.
- Eczema: Atopic dermatitis is an itchy rash caused by an allergen.
- Allergy from certain foods.
- Allergic rhinitis: Indoor allergens like dust and pets, as well as outdoor allergens like pollens and molds, can cause sneezing, a runny nose, sniffling, and nasal tube edema.
Some examples of Autoimmune diseases are
- Type 1 Diabetes: The most common kind of diabetes. In this immune system targets the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone that takes sugar from the bloodstream and converts it to energy.
- Rheumatoid arthritis : Swelling and abnormalities of the joints are common symptoms of this type of arthritis. Some people with rheumatoid arthritis have an auto-antibody called rheumatoid factor in their blood.
- Lupus : This condition affects the lungs, kidneys, and skin, among other body components. Auto-antibodies of various sorts can be seen in the blood of lupus patients.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) : In this the immune system destroys nerve cells, resulting in pain, blindness, weakness, poor coordination, and muscle spasms, among other symptoms.
Nobody knows for sure what causes autoimmune diseases, but a variety of factors appear to have a role. Learn everything you can about your immune system disorder if you have one. Consult your doctor immediately to keep it under control.
Immunity & current variants of Covid-19 : A big concern
With the introduction of many COVID-19 variants, including worrisome variants like Delta and Omicron, also a growing number of COVID-19 patients worldwide, it’s critical to comprehend the disease’s developing path.
Increased transmissibility and the ability to circumvent immunity provided by previous infection or vaccination are assumed to be driving the rise in Omicron infections (immune evasion phenomenon)
Immune evasion appears to have a larger role in Omicron transmission than increased transmissibility, according to epidemiological research and various scientific experiments. Furthermore, as compared to Delta and other preceding variants, Omicron is expected to impair, but not entirely compromise, immunity acquired by prior infection or vaccination.
However, studies show that those who have been vaccinated and given a booster dose or who have been previously infected are more likely to be protected against Omicron.
Whether it’s Omicron, Delta, or other COVID-19 viral variations, unvaccinated persons are always the most dangerous. They are the most vulnerable to transmission and are more likely to become infected and hence spread the virus.
The vaccine offers the best protection against serious illness and diseases for everyone. Vaccines, while generally efficient, are not without flaws, and vaccine-related illnesses can occur. Immunization is the most effective strategy to protect yourself, your family and your community in general.
Covid-19 & Immune System :
Concerns about COVID-19 have prompted an increase in online searches for information on how to protect yourself from this virus. What more can we do to improve health besides appropriate handwashing?

Vaccination is the most efficient technique to boost our immune systems and protect ourselves from diseases. Vaccination also effectively prevents the spread of a virus among humans.
Vaccination, often known as immunization, works by exposing the body to a virus that has been weakened or killed, or to its invalid toxins. The body will learn how to combat disease without getting sick. This is also known as active immunization, and it results in the creation of disease-specific antibodies.
In the instance of passive immunization, the patient obtains antibodies that were made by another person’s immune system to combat the disease.
Covid-19 : Immune System Boosters
Zinc (Important for wound healing) : Lean meats, seafood, milk, whole grains, beans, seeds & nuts.
Vitamin C (Protect cells from oxidative stress, a product of infection or chronic inflammation) : Broccolli, oranges, strawberries, tomatoes & guava.
Iron (Aids in non-specific immunity, the body’s first line of defense : Lentis, Spinach & White Beans.
Vitamin E (Helps protect cells from oxidative stress) : Nuts, seeds, wheat germ &green leafy vegetables.
Vitamin A (Helps regulate immune response) : Sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach & mangoes.
Vitamin B 6 (Supports more efficient reactions between different parts of our immune system ) : Green vegetables & chick peas.

Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
Great information shared.. really enjoyed reading this post thank you author for sharing this post .. appreciated
Great information shared.. really enjoyed reading this post thank you author for sharing this post .. appreciated
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
Awesome! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this post
I am truly thankful to the owner of this web site who has shared this fantastic piece of writing at at this place.
This post has been a great resource for me. It’s well-written and covers the topic comprehensively. Thank you for sharing your knowledge and expertise!
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.